Electricians Helping Other Electricians Sort Facts And Thumbrules


By Lloyd Mills
•
October 25, 2024
Can You Really Get Shocked from a Neutral Wire? Short answer: No, you can't. A common misconception is that you can get an electric shock from touching a neutral wire. This is a myth that likely stems from the idea that electricity flows in a complete circuit, and the neutral wire is part of that circuit. However, the neutral wire serves a different purpose than the hot wire.

By Lloyd Mills
•
October 14, 2024
Is the inspector the AHJ? AHJ (or AWJ) is the authority having jurisdiction (or authority with jurisdiction). That brings up two questions: What authority and what jurisdiction? The authority or jurisdiction to enforce a standard is not ever the same authority to adopt that standard. To adopt any standard, there are requirements such as voting or publishing. No single person could ever hold that authority over another person. While an inspector may have influence, their role as code enforcement is to enforce that standard, not create it. Enforcing any standard or law that has not been adopted removes qualified immunity. The role of inspector is not adoption. Interpreta tion In many cases an inspector may interpret standards for electricians but their interpretation of a standard is not the standard, it's literally their own interpretation of it and not ever enforceable.
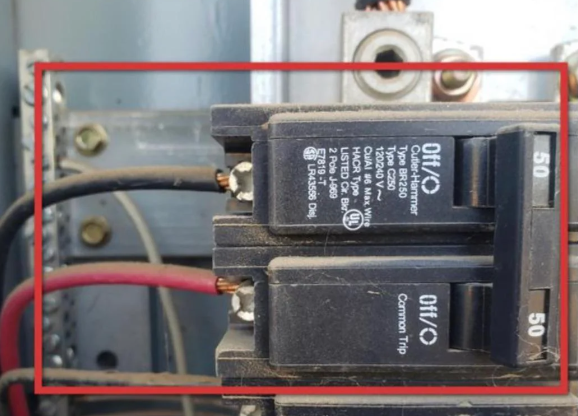
By Lloyd Mills
•
October 4, 2024
Understanding Breaker Protection and Load Types When dealing with certain types of loads, like motor loads, welders, or HVAC equipment, the traditional rule of matching breaker size to wire size might not be strictly necessary. This is because these loads often have built-in protective mechanisms that can handle overcurrent protection more effectively than a standalone breaker. The Three Functions of a Breaker Ground Fault Protection: This protects against electrical shocks by detecting imbalances in current flow. Short Circuit Protection: This protects against sudden surges of current that can damage equipment or cause fires. Overcurrent Protection: This protects against excessive current that can overload circuits and cause damage. Specialized Load Protection For specific loads like motors, welders, and HVAC equipment, additional protective measures are often in place: Motor Starters: These devices typically have built-in thermal overload relays that are specifically designed to protect motors from excessive current. HVAC Equipment: Many HVAC units use thermally protected motors, which have built-in protection against overheating. The Role of the Breaker In these cases, the breaker's primary function becomes to provide ground fault and short circuit protection. Overcurrent protection is handled by the built-in mechanisms within the load itself. This allows for more flexibility in breaker sizing.

By Lloyd Mills
•
October 3, 2024
Short answer: Yes, it's generally okay. While it might seem counterintuitive, using a 15 amp receptacle on a 20 amp circuit is often permissible. This is because the 15 amp receptacle has a built-in safety feature called a rejection feature. Understanding the Rejection Feature The rejection feature in a 15 amp receptacle prevents the insertion of a 20 amp plug into a 15 amp receptacle. This helps to ensure that appliances requiring a 20 amp circuit are not plugged into a circuit that cannot provide the necessary power. However, it does not prevent the insertion of a 15 amp plug into a 20 amp receptacle. Why is This Safe? Circuit Breaker Protection: Even if you plug a 20 amp appliance into a 15 amp receptacle somehow, the circuit breaker will protect the circuit from overload. If the appliance draws more current than the circuit can handle, the breaker will trip, preventing damage to the wiring and appliances. Appliance Safety: Modern appliances are designed to be compatible with various circuit capacities. They often have built-in safety features to prevent damage if they are plugged into a circuit that is underpowered.
